When we talk about threats in the digital world, the first thing we usually think of are viruses and malware. But there are many more ways cybercriminals can attack us. From phishing to ransomware, cyber attacks are constantly evolving, which is why it is important to understand how to protect yourself. In this blog, we discuss the different types of cyber attacks and provide tips on how to protect yourself and your online data from these threats. By following these practical tips, you can ensure that your online security is no longer a source of worry.
Computer malware has been around since the 1970s, when the first computer worm virus spread via ARPANET, a precursor to the Internet. In the 1980s, the number of viruses increased rapidly, especially with the popularity of floppy disks that users exchanged among themselves.
A computer virus back then was usually still relatively simple, and the damage was often limited. The 1990s brought a new wave of viruses that, for example, forwarded stolen passwords or held entire systems hostage. In the 2000s, malware became more sophisticated and bots and rootkits became a reality.
Today, malware attacks are often automated and targeted at data that are financially or strategically lucrative for cybercriminals. Although many now include sophisticated antivirus programs, malware remains a threat to all Internet users.

Types of Cyber Attacks
Just a list of the most common forms of cyber attacks.
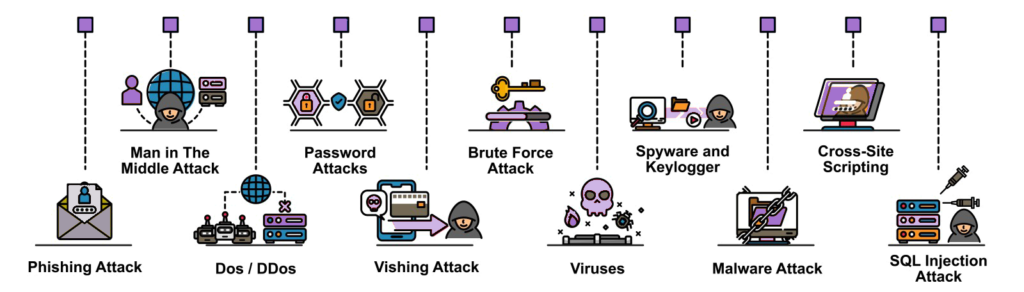
Phishing: attackers use fake emails or websites to lure users into giving up sensitive information (such as passwords or credit card numbers).
Protect yourself by carefully checking the source of any e-mail or website about which you have doubts, and without checking the sender or website, do not reveal any personal information. Anyway, it’s better not to log into your account from an email link. Just use your browser and log into your familiar environment there.
Malware: which is any type of malicious software designed to harm your computer, steal data or gain unauthorized access to your devices.
Protect yourself by avoiding downloading attachments from unknown sources and be careful when visiting suspicious websites. Possibly you can Install a reliable antivirus software and keep it up-to-date. Often the standard antimalware apps are best such as defender for Windows and XProtect for the Mac.
DDoS attacks: this is a coordinated attempt to overload a website or server by flooding it with traffic from multiple sources. DDoS attacks can target businesses to overload and thus disrupt their websites or online services. This can be done by competitors, activists, hackers or criminals with financial motives.
Protect your website by using a reliable web hosting service that offers DDoS protection, checking your website performance regularly and setting up a backup hosting solution in case of an attack. Many websites use cloudflare for this
In the gaming community, DDoS attacks can also be used to take a player or group of players offline, preventing them from participating in online games or tournaments. This can be done by rival players, hackers or others with the intention of cheating.
A gamer can use a Virtual Private Network (VPN): By using a VPN, the gamer’s IP address is hidden and harder for an attacker to trace. It can also help encrypt the connection and increase security
Ransomware: a form of malware that encrypts your files and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key.
Protect yourself by regularly backing up your files to an external hard drive or cloud service, being careful when opening attachments or clicking on links in emails and never paying the ransom.
Perhaps the best tip to prevent a cyber attack is to update all your devices regularly. Be sure to install an update immediately.